Identifying a Pacific Madrone might seem daunting, but you can easily recognize this beautiful tree with the right knowledge. Pacific Madrone (Arbutus menziesii) is a broadleaved evergreen tree native to the western coastal areas of North America, from British Columbia to California. It is one of the largest of about 14 species of Arbutus in the world and is a member of the heath family (Ericaceae).
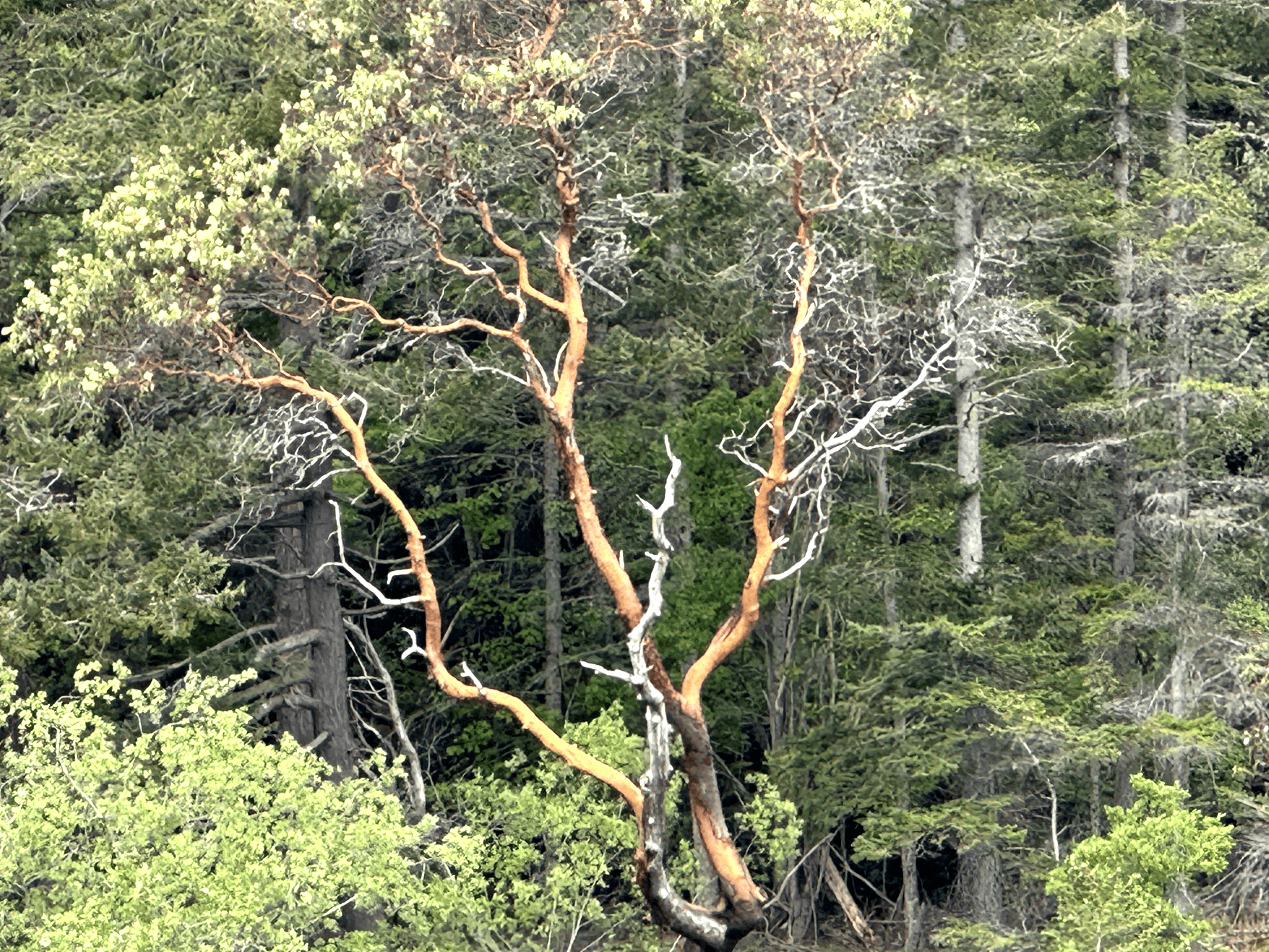
One of the Pacific Madrone’s most distinguishing features is its bark. Its upper red-brown bark peels each summer in thin strips to reveal smooth, greenish-yellow bark that ripens into a deep, dark red color. This peeling bark gives the tree a unique and beautiful appearance. The tree also produces white, fragrant, urn-shaped flowers that dangle in clusters at the ends of branches and scarlet red, bumpy berries that ripen in the fall and may last into early winter.
If you’re wondering how to identify a Pacific Madrone, keep reading to learn more about the characteristics of this beautiful tree.
Key Takeaways
- The Pacific Madrone is a broadleaved evergreen tree native to the western coastal areas of North America.
- The peeling bark, white urn-shaped flowers, and scarlet red berries are distinguishing features of the Pacific Madrone.
- Understanding the identifying characteristics of the Pacific Madrone can help you recognize this beautiful tree.
Table of Contents
Key Characteristics for Pacific Madrone Identification
If you are wondering how to identify a Pacific Madrone, there are several key characteristics to look for. These include the leaves, bark and trunk, flowers and fruit, and the tree’s form and size.
Leaves
Pacific Madrone leaves are evergreen and glossy, with a leathery texture. The leaves are oval-shaped and pointed, with a smooth edge. The leaves are dark green on top and lighter green on the underside.
Bark and Trunk

One of the Pacific Madrone’s most distinctive features is its bark. It is smooth and reddish-brown when young, but as the tree ages, the bark peels away in thin strips to reveal a greenish-yellow bark that ripens into a deep, dark red color. The trunk of the Pacific Madrone is typically straight and slender, with a smooth texture.
Flowers and Fruit
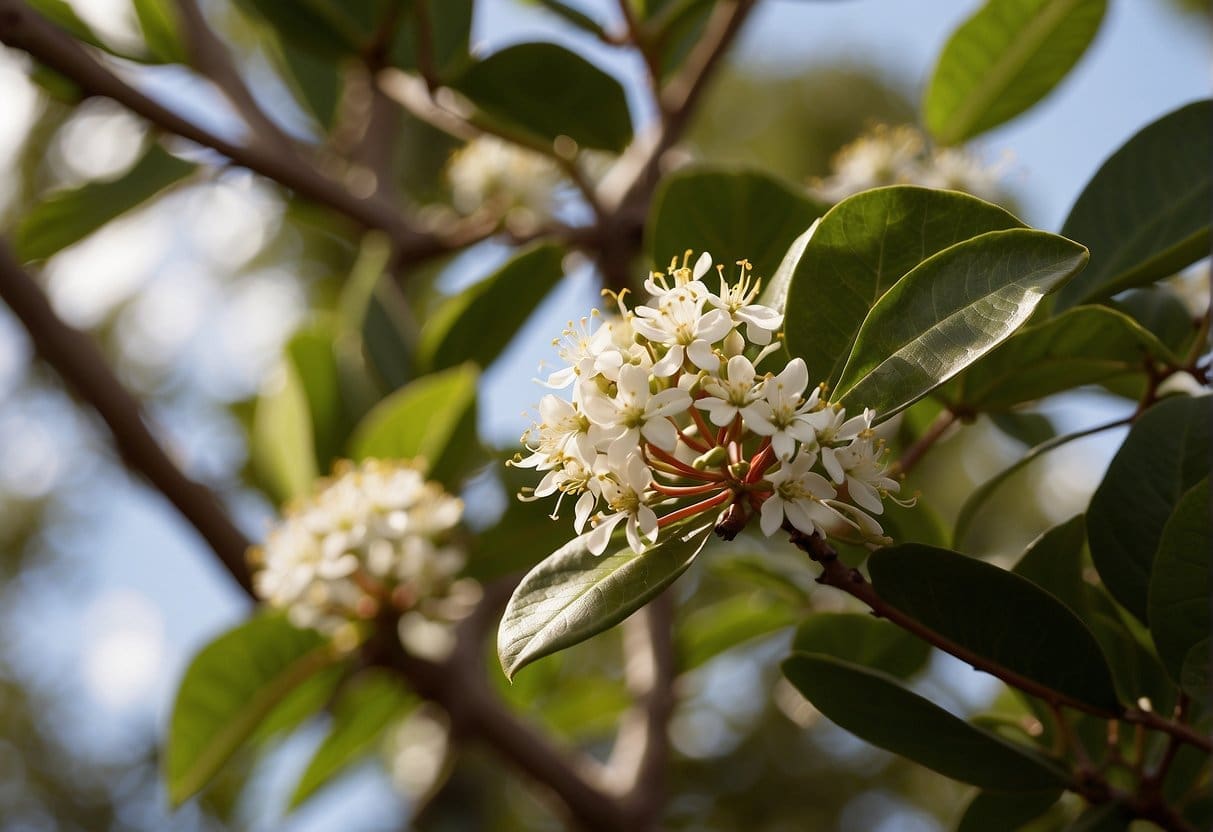

The Pacific Madrone produces white, fragrant, urn-shaped flowers that dangle in clusters at the ends of its branches in the spring and early summer. In the fall, the tree produces scarlet red, bumpy berries that are 8-12 mm in diameter. These berries are edible but rather bland.
Form and Size
The Pacific Madrone is a relatively slow-growing tree that can reach heights of 50 to 100 feet or more in the wild but usually tops out at only 20 to 50 feet in home gardens. It has a broad, spreading crown with a twisted, gnarled appearance. The tree is also known for its attractive, peeling bark and unique form.
Examining the characteristics of the Pacific Madrone, including its leaves, bark and trunk, flowers and fruit, and form and size, you can easily identify this distinctive tree. The Pacific Madrone is a beautiful and unique addition to any landscape with its evergreen leaves, white flowers, and red berries.
Exploring the Habitat and Distribution of the Pacific Madrone
Knowing where to look is important if you’re interested in identifying a Pacific Madrone. This section will cover the species’ geographical range, preferred soils and climate, and elevation zones.
Geographical Range
The Pacific Madrone (Arbutus menziesii) is a tree native to the western coastal areas of North America, stretching from British Columbia to San Diego. It is commonly found in the Coast Range of California, Oregon, and Washington, as well as on Vancouver Island.
Preferred Soils and Climate
Pacific Madrones thrive in well-drained soils, particularly rocky and porous ones. They prefer soils derived from glacial deposits of porous sands and gravels and hard till in the north, volcanic tuffs and metamorphosed sedimentary and volcanic rocks in the Klamath Mountains, and volcanic and sedimentary rocks in the California Coast Ranges.
They also prefer a Mediterranean climate, with mild, wet winters and dry summers. This climate is characterized by cool, wet winters and warm, dry summers.
Elevation Zones
Pacific Madrones are typically found at elevations between sea level and 5,000 feet, although they can grow at higher elevations in some areas. They are most commonly found in the Siskiyou Mountains, where they can grow at elevations of up to 7,000 feet.
If you’re looking to identify a Pacific Madrone, your best bet is to head to the coastal areas of California, Oregon, Washington, or Vancouver Island. Look for well-drained, rocky soils and a Mediterranean climate, and look for these trees at elevations between sea level and 5,000 feet.
Understanding the Ecology and Wildlife Relationships of Pacific Madrone

Pollinators and Seed Dispersal
Pacific madrone is a valuable resource for pollinators such as bees and hummingbirds. In May, the tree produces sweet-smelling flowers that attract many honeybees. Hummingbirds are also attracted to the flowers and help in pollination. The tree’s berries ripen in autumn and last until December, providing food for birds and other wildlife. The seeds are dispersed by birds, mammals, and insects, helping to spread the tree’s range.
Coexisting Flora and Fauna
Pacific madrone coexists with a variety of flora and fauna. The tree is found in open woodlands and can grow alongside other trees such as Douglas fir, tanoak, Oregon white oak, California black oak, western hemlock, and redwood. The heath family, which includes salal, is also commonly found in these areas. The tree’s smooth bark provides a habitat for insects, and the berries attract cedar waxwings, pigeons, quail, and raccoons.
Ecological Importance
Pacific madrone is ecologically important as it plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. The tree provides a habitat for a variety of wildlife, including bears, mule deer, and other mammals. The tree’s leaves and bark provide shelter for insects and other small animals. The tree’s root system helps to prevent soil erosion and provides a source of nutrients for other plants. Pacific madrone is also important economically, as it is used for furniture, flooring, and other decorative purposes.
The Pacific madrone is a valuable resource for pollinators and wildlife, coexisting with a variety of flora and fauna. The tree’s ecological importance cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
Best Practices for Cultivating and Caring for Pacific Madrone
Growing a Pacific Madrone tree can be a rewarding experience. Here are some tips to help you cultivate and care for your tree.
Planting and Growth Conditions
Pacific Madrone trees thrive in full sun and well-draining soil. They are frost-resistant and can tolerate moderate drought. When transplanting seedlings, handling the roots gently to avoid damage is important.
Disease and Pest Management
Madrone Canker and Root Rot, caused by Phytophthora cactorum and Nattrassia mangiferae, respectively, are common diseases that can affect Pacific Madrone trees. To prevent these diseases, avoid overwatering and ensure proper drainage. Pests like spider mites and aphids can also infest the tree. Regularly inspecting your tree and treating any infestations can help prevent damage.
Conservation and Restoration Efforts
Pacific Madrone trees are an important species for birds and wildlife in the Pacific Northwest. Conservation and restoration efforts are crucial to protecting this species. Planting Madrone trees in areas where they have been lost due to development or wildfires can help restore their populations.
Pacific Madrone trees are a beautiful and valuable addition to any landscape. With proper care and attention, your tree can thrive for years to come.
Cultural and Historical Significance of the Pacific Madrone

Indigenous Uses
The Pacific Madrone played an important role in the culture and lifestyle of the Saanich people, who used its bark, leaves, and berries for medicinal and nutritional purposes. The bark was used to make astringent and antiseptic poultices for treating cuts, burns, and wounds. The leaves were used to make tea that helped alleviate cold and flu symptoms. The berries were eaten fresh or dried and were a source of food for birds and other animals.
Modern Applications
Today, the Pacific Madrone is highly valued for its unique and beautiful wood used in furniture making, veneer, and decorative items. The tree is also used in cider production due to its high sugar content. The Pacific Madrone has been introduced as an ornamental tree in the Mediterranean due to its attractive appearance and drought tolerance.
Conservationists and researchers are also interested in the ecology of the Pacific Madrone. The tree is an important part of the Pacific Northwest’s forest ecosystem, providing habitat for a variety of wildlife and contributing to the region’s biodiversity. The National Register of Big Trees recognizes the Pacific Madrone as the largest broadleaf tree in the United States.
Oregon State University and Portland’s Hoyt Arboretum are also actively involved in studying and conserving the Pacific Madrone. The university’s Department of Forest Ecosystems and Society conducts research on the tree’s ecology and genetics, while the arboretum maintains a collection of Pacific Madrone specimens for public education and enjoyment.
The Pacific Madrone has played an important role in the cultural and historical heritage of the Pacific Northwest. Today, it continues to be valued for its unique properties and contributions to the region’s ecology and economy.
Addressing Challenges and Threats to Pacific Madrone
Environmental Threats
Identifying Pacific Madrone can be challenging due to their habitat’s decline. Fungi and diseases, such as madrone root diseases, can cause cankers and discolored bark on the tree trunk, leading to the loss of foliage and small, curled leaves. These environmental threats can reduce the lifespan of the tree and impact its growth.
Conservation Status
The Pacific Madrone is not currently listed as threatened or endangered, but conservation efforts are still necessary to protect the species. Populations of this keystone species are already threatened by climate change, pests, and diseases. For example, madrone leaf blight is a major disease affecting western Washington and Oregon trees. Identifying populations that are most tolerant to leaf blight is a priority for conservation efforts.
Southern California has also seen a decline in Pacific Madrone populations due to urbanization and habitat destruction. The tree’s longevity and resistance to gravity make it a valuable addition to the landscape, and conservation efforts are necessary to preserve the species for future generations.
Identifying a Pacific Madrone can be challenging due to environmental threats and the decline in their habitat. However, conservation efforts can help protect the species from further decline.
Pacific Madrone FAQs: Everything You Need to Know
What are the distinguishing characteristics of Pacific Madrone leaves?
Pacific Madrone leaves are evergreen, leathery, and glossy. They have a dark green upper surface and a lighter green underside. Their edges are smooth with a wavy margin, and their shape is oblong to elliptical.
What type of fruit does the Pacific Madrone produce?
The Pacific Madrone produces small, round, edible, red berries that are rather bland. They mature in late summer and are an important food source for birds and mammals.
In which habitats are Pacific Madrone trees typically found?
Pacific Madrone trees are typically found in dry, rocky soils in coastal and foothill regions of the Pacific Northwest. They are also found in oak woodlands, chaparral, and mixed evergreen forests.
How can one differentiate between a Pacific Madrone and a Manzanita?
Pacific Madrone trees have smooth, reddish-brown bark that peels away to reveal a greenish layer underneath. Manzanita trees, on the other hand, have smooth, reddish-brown bark that does not peel away.
What are the notable uses of Pacific Madrone trees?
Pacific Madrone wood is hard, durable, and beautiful reddish-brown in color. It is used for furniture, flooring, and decorative woodwork. The berries are also used to make jams and jellies.
What are some unique features of Pacific Madrone trees?
Pacific Madrone trees have a striking appearance with their smooth, reddish-brown bark and twisting branches. They are also evergreen, shedding their leaves sporadically every two years. Additionally, they can regenerate from their roots if their above-ground portion is damaged or destroyed.

